Back to General Dermatology
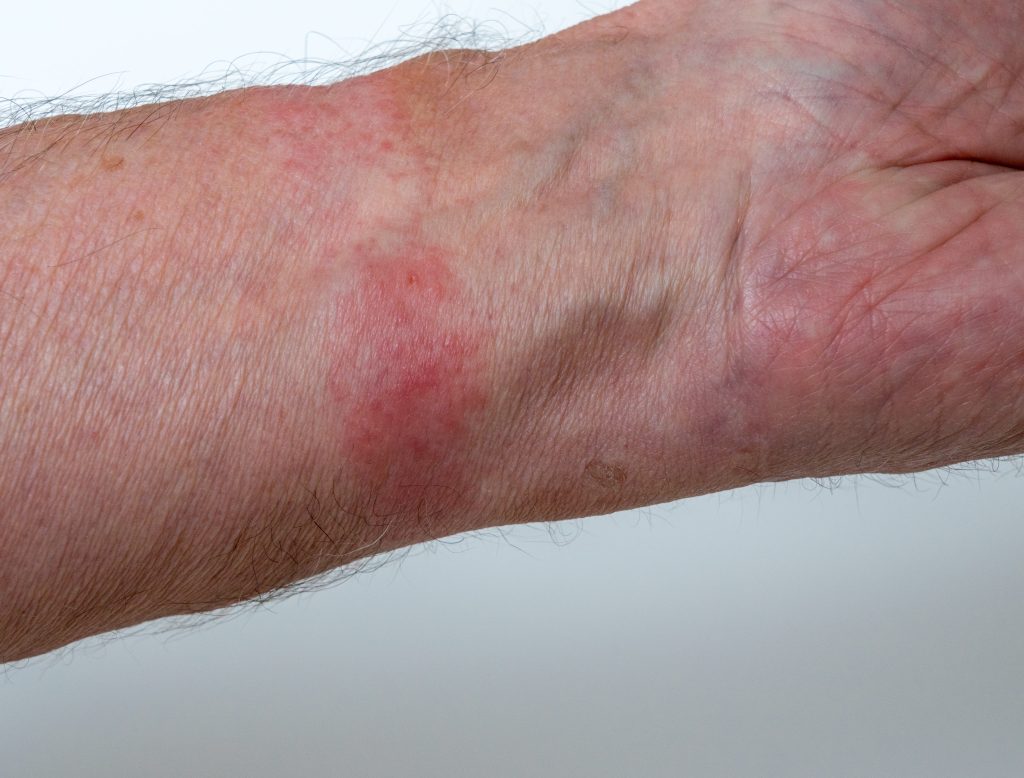
What is Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a type of delayed hypersensitivity reaction that develops when the immune system reacts to a specific substance, known as an allergen, upon contact with the skin. Unlike irritant contact dermatitis, which occurs due to direct skin irritation, allergic contact dermatitis involves an immune response that leads to inflammation.
Common Allergens
Allergic contact dermatitis can be triggered by a wide range of substances, including:
- Metals such as nickel (commonly found in jewelry), gold, and cobalt
- Fragrances and perfumes
- Cosmetics and skincare products
- Latex
- Poison ivy, oak, and sumac
- Certain medications
- Chemicals in household products like detergents, cleaning agents, and solvents
Symptoms of Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Itchy and red skin: Allergic contact dermatitis typically causes intense itching and redness in the affected area.
- Rash and blisters: The skin may develop a rash with small bumps or blisters that can ooze, crust over, or become scaly.
- Swelling and inflammation: The affected skin may appear swollen and inflamed.
- Dryness and cracking: The skin can become dry, cracked and more susceptible to secondary infections.
Treatment and Management
- Avoidance of allergens: The primary approach to managing allergic contact dermatitis is to identify the causative agent and avoid exposure. This may involve reading product labels, selecting hypoallergenic options, and using protective measures such as gloves when handling irritants.
- Topical corticosteroids: Prescription strength creams or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms during flare-ups.
- Moisturizers: Regularly applying moisturizer helps to hydrate the skin, reducing dryness, itchiness, and discomfort.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can help to alleviate itching and reduce allergic reactions.
- Immune modulating creams: In certain cases, immunomodulatory medications, such as calcineurin inhibitors, may be prescribed to manage severe or chronic allergic contact dermatitis.
- Systemic treatments: Immunomodulatory medications can help decrease allergic contact dermatitis. These treatments range from oral steroids to more targeted immune therapy, such as Dupixent.
Allergic contact dermatitis can be a bothersome and uncomfortable condition, but with proper management strategies and avoidance of triggers, individuals can significantly reduce symptoms and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you may have allergic contact dermatitis, or are experiencing persistent skin reactions, please call and schedule an appointment with one of our providers for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
