Back to General Dermatology
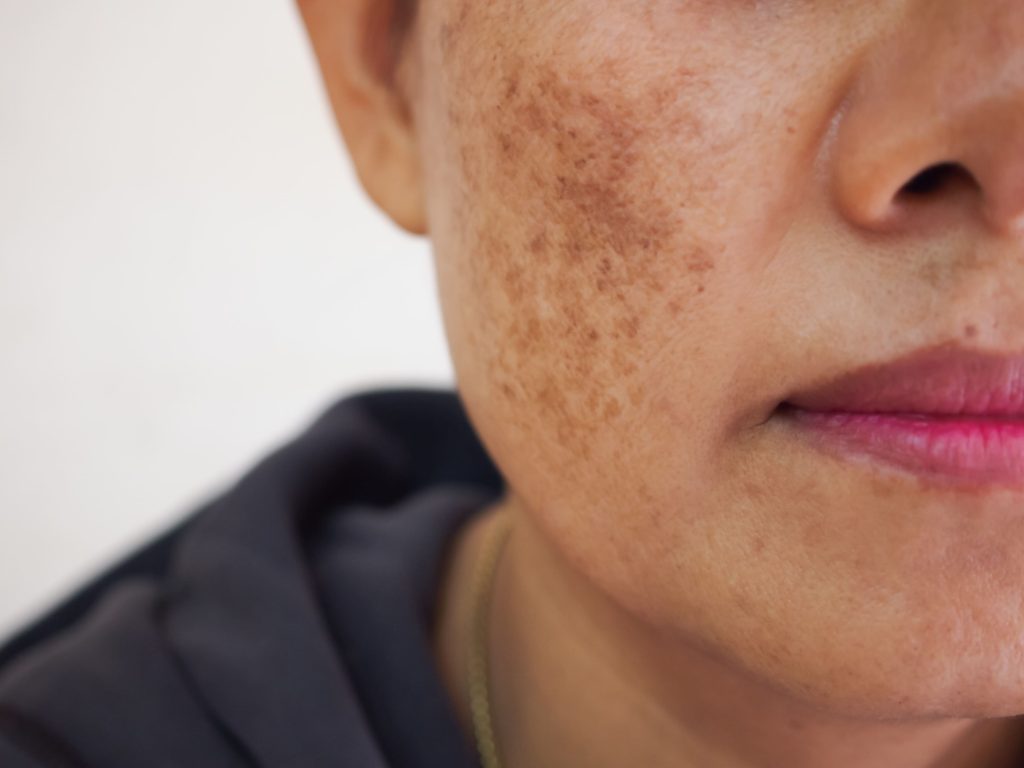
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition that results in the development of brown or grayish patches on the face. It is more common in women. Melasma occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. It is influenced by various factors, including sun exposure, hormones (estrogen), heat, and genetic predisposition.
Symptoms and Patterns
- Hyperpigmented patches: The primary symptom of melasma is the presence of dark, irregularly shaped patches on the face. These patches typically have defined borders and can vary in size and intensity.
- Distribution patterns: Melasma often appears symmetrically on both sides of the face, such as on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip.
Causes and Triggers
- Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates the production of melanin, which can worsen melasma. Sun exposure without proper protection can trigger or exacerbate the condition.
- Hormonal factors: Elevated hormone states, specifically high estrogen stages of pregnancy and taking oral contraceptive medications, can stimulate the production of melanin and contribute to the development of melasma.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of melasma is a risk factor, suggesting a genetic component of melasma.
Treatment Options for Melasma
- Sun protection: Sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF), broad-spectrum coverage, and physical blockers ( zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) should be worn. Sun-protective clothing and accessories, such as wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses, are also beneficial.
- Topical treatments: Prescription creams containing the active ingredients hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroids, and/or azelaic acid may be recommended to lighten the patches and even out the skin tone. Cosmeceutical products including antioxidants and skin brighteners may also help improve melasma.
- Procedures: Certain dermatological procedures, such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser therapy (fractional ablative CO2 laser), can be used to reduce the appearance of melasma. Make sure to select a practitioner experienced in treating melasma.
- Maintenance therapy: Even after achieving improvement, it is essential to continue sun protection and maintenance therapy to prevent recurrence and manage the condition long-term.
Melasma can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right approach, it is possible to improve the appearance of the skin and reduce the impact of the skin discoloration. If you are concerned about melasma or want guidance on the most suitable treatment options for your skin, please call to schedule an appointment with one of our highly skilled board-certified medical providers for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
