Back to General Dermatology
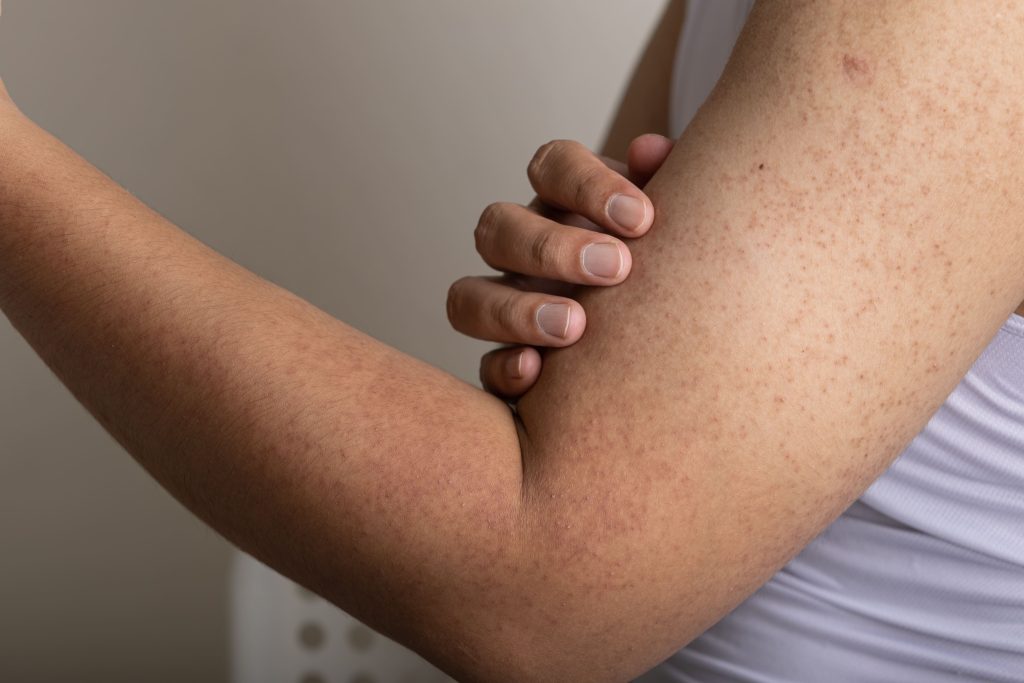
What is Keratosis Pilaris?
Keratosis pilaris is a common, benign skin condition characterized by small, rough bumps on the skin’s surface. It occurs when excess keratin builds up and clogs the hair follicles. While the exact cause is unknown, keratosis pilaris is often associated with genetic factors and tends to be more common in individuals with dry, sensitive skin or eczema.
Symptoms of Keratosis Pilaris
- Small bumps: The primary symptom of keratosis pilaris is the presence of small, rough bumps on the skin. These bumps are typically flesh-colored or slightly red and may resemble goosebumps or the texture of sandpaper. The background is often erythematous, or pink appearing.
- Dryness and roughness: The affected skin areas may feel dry, rough, and occasionally itchy.
- Appearance on specific body parts: Keratosis pilaris most commonly appears on the upper arms, but may also affect the thighs, buttocks, and occasionally the face. It is usually symmetric, affecting both sides of the body equally.
Causes and Triggers
- Genetic factors: Keratosis pilaris often has a genetic component and a family history of the condition is common.
- Dry skin: Individuals with dry, sensitive skin tend to be more susceptible to developing keratosis pilaris.
- Certain medical conditions: Keratosis pilaris is often associated with other skin conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) or ichthyosis vulgaris.
- Climate and environmental factors: Cold, dry climates or low humidity levels can exacerbate the symptoms of keratosis pilaris.
Treatment and Management
- Avoid physical exfoliation: Physical exfoliation with scrubs or brushes often aggravate the condition.
- Moisturization: Keeping the skin well-hydrated with emollient-rich moisturizers can help reduce dryness and soften the rough bumps.
- Topical treatments: Creams or lotions containing chemical exfoliants can help smooth the skin and reduce the appearance of keratosis pilaris. These chemical exfoliants include urea, alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs), and salicylic acid.
- Prescription medications: In severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical retinoids or corticosteroids to alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Maintaining a healthy skincare routine, avoiding excessive hot showers or harsh soaps, and protecting the skin from dry environments can help manage keratosis pilaris.
Keratosis pilaris is a common, benign skin condition that primarily affects the appearance and texture of the skin. While it may not be curable, individuals can effectively manage and minimize the symptoms with appropriate treatment. If you are concerned about keratosis pilaris or want guidance on the most suitable treatment options for your skin, please call to schedule an appointment with one of our highly skilled board-certified medical providers for personalized treatment options and advice.
